Insurers who are prepared and who manage their IT investments with a business mindset of ecosystem integration will be prepared to convert these challenging days into a growth opportunity.
The global insurance market, like so many others, is adjusting to reduced business activity in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. Insurers are looking to deliver transformative projects quickly and at lower prices. While insurance CIOs are work to navigate their IT budgets and InsurTech priorities, they also have an opportunity to manage costs with a mindset aimed at innovation.
Technology budgets (including IT software, hardware, services, and staff) are commonly set as a portion of premiums, growing or contracting in accordance with incoming premiums. Although premiums are facing new challenges, budgetary pressures may provide opportunities to rethink and refresh technology’s role in strategic and business needs.
Insurers’ IT Spending Trajectory
In response to the pandemic, insurers appear to be delaying big legacy system replacement and transformation programs. As detailed in the September 2020 Celent report IT Spending in Insurance, new technology investments will be targeted toward digitized channels for sales growth and engaging customer experiences, productivity advances, and data/AI techniques aimed at improving underwriting results.
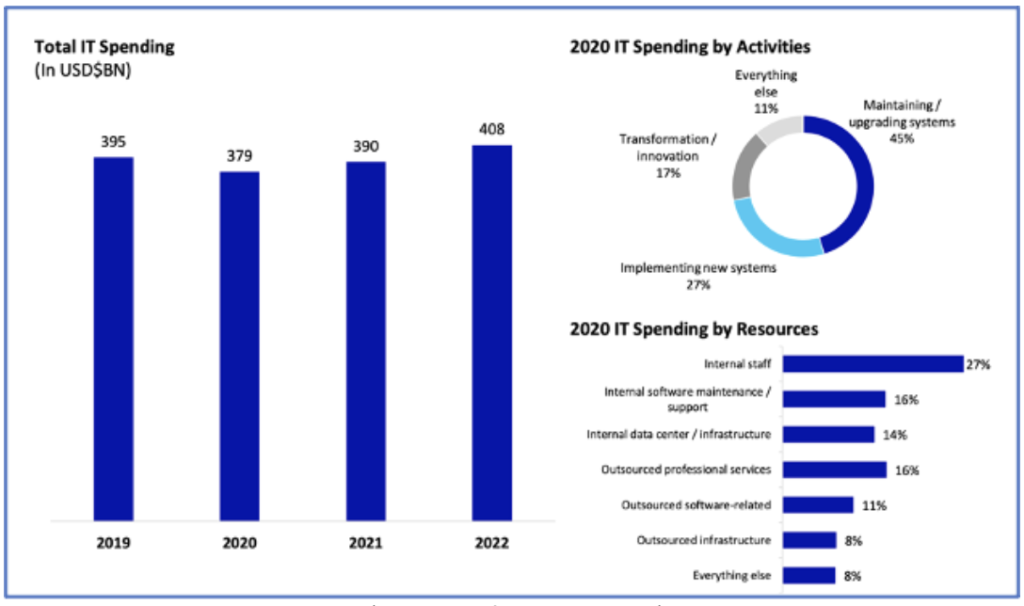
In 2020, insurers are spending an estimated US$380BN in IT; that number is estimated to overpass USD$400BN by 2022. North America is the largest market in terms of premiums (life and non-life) and IT spending, with an estimated 39 percent of global IT spending; Asia-Pacific represents 31 percent of global IT spending; Europe Middle East and Africa (EMEA), 28 percent; and the Latin American insurance market represents only 2 percent of global IT spending. System maintenance and upgrades draw the largest percentage (45 percent) of this spend, followed by new system implementation (27 percent), and transformation/innovation (17 percent).
Increasingly, insurers are looking to the cloud as a means of lowering IT costs. Greater cloud adoption is one of the primary methods of implementing efficiencies in software delivery. Open source software and agile technologies also play a role in cost reduction efforts. While cloud implementation may take slightly different shapes across regions, it’s clearly growing as a priority for insurers around the globe. In North America, insurers are increasingly making cloud a top priority in the framework of core technology transformation; it is being leveraged with platform-as-a-service (PAAS), DevOps, DataOps, MLOps, and artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) capabilities. In Europe, cloud is among the technologies being relied on for efficiencies and lowered engineering costs. In Asia-Pacific (including emerging, fast growth, and mature markets), cloud native computing in a critical component of core application modernization for insurers.
Four Trends in IT Spending in the Insurance Market
As CIOs address the need to keep expenses flat or to lower them, technology renewal remains focused on productivity and on the cost benefits that are possible with new technologies. With this in mind, insurers are likely to allocate their IT investments in alignment with the following four technology trends.
1. Insurers are relying on technology investments to innovate along the traditional value chain. For every step in the insurance sales and delivery process—prospecting, product recommendations, analytics, risk modeling, loss estimation, claims processing, renewals, and more—IT improvements can enhance the overall experience for all parties. Insurers recognize this and are investing accordingly.
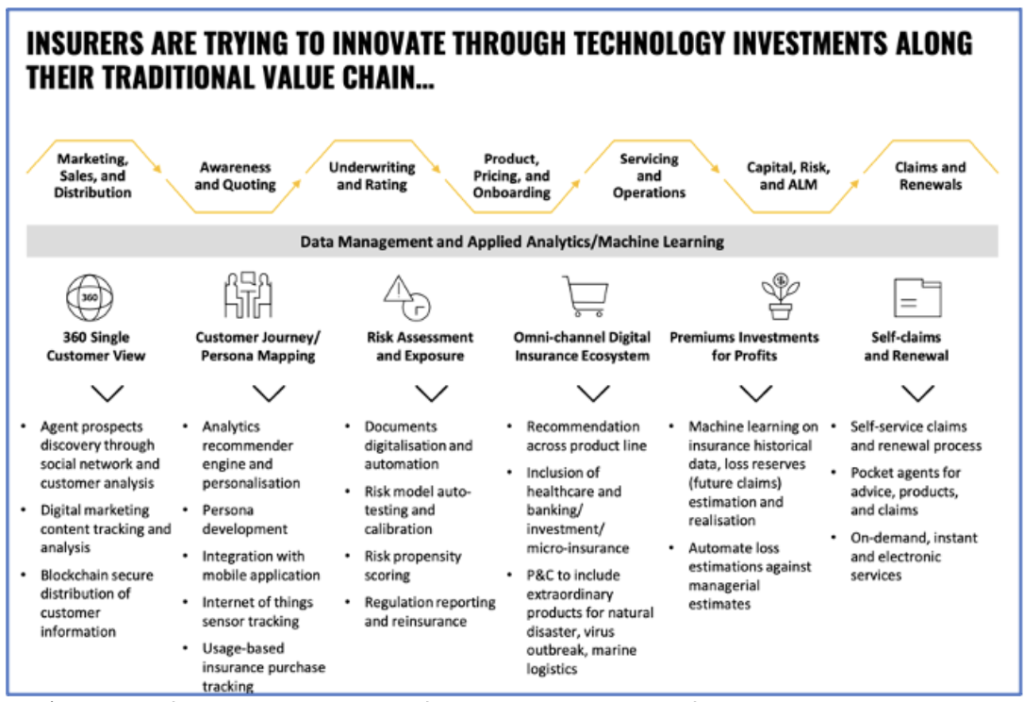
2. Automation and customer experience improvements are fundamental for improving value. In the coming five years, operations (middle and back offices) will move to adopt API microservice architecture, priming optimization through ML, and integrated ecosystem with banking, for example. Business model (front office) enhancements will come through robust customer assistant offerings such as on-demand insurance purchase availability, mobile first delivery, rule-based chatbots, and conversational bots for insurance advisory, documentation, and assessment.
3. Insurers will expand their integrated ecosystems. The insurer of tomorrow will embrace integrated ecosystems—supported through AI-powered insurers, hybrid agents, and customer service—to support customer empowerment and self-service across regional operations. The requisite technology infrastructure for this approach relies on microservices and containers, open data, and API integrations, all built upon a foundation of cloud and edge computing.
4. Future leading-edge insurers will draw on certain sets of technologies to solidify their advantages. Comprehensive integrated ecosystems will help future-focused insurers, insurtechs, and IT vendors stand out. Cloud and edge computing can support enhanced customer experiences (e.g., though onboarding, on-demand services, and customer experience design). Areas of empowerment include the domains of agriculture, banking, healthcare and medical services, insurance, supply chain, telecom, and wealth management.
Moving Past the Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic clearly had significant, negative impacts in insurance. Health uncertainty created tighter underwriting for life and health products during a time of increased demands. Certain classes of business saw an immediate downturn, as was the case for sports/events insurance. But looking forward, opportunities will appear. In response to the pandemic’s impact (possibly from consumer and corporate attitudes to coverage or through increased interest in private health coverage or enhanced business coverage), the overall demand for coverage is likely going to grow. Insurers who are prepared and who manage their IT investments with a business mindset of ecosystem integration will be prepared to convert these challenging days into a growth opportunity.
Source: Insurance Innovation Reporter

Cowbell Introduces GenAI-Powered Underwriting Tool to Enhance Efficiency
Cowbell, a leading provider of cyber insurance for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), has launched Prime Tech with Cowbell Co-Pilot, a generative AI solution designed to streamline underwriting within its Prime Tech offering.

Capitola Insurance Officially Rebrands as Flow Specialty
Flow Specialty, previously known as Capitola Insurance, has announced its official rebrand. Supported by Munich Re Ventures and Lightspeed Venture Partners, Flow Specialty is poised to elevate the specialty wholesale insurance market with its innovative approach.

Chubb Announces Q1 2024 Net Income Increase and P&C Combined Ratio of 86%
Global insurer Chubb reported a net income rise of 13.3% to $2.14 billion in the first quarter of 2024, boosted by strong performances in its property and casualty (P&C) and life insurance sectors.